On behalf of 2.1 million Americans living with limb loss and limb difference and the 28 million additional Americans that are at risk of entering the limb loss community, the Amputee Coalition recently sent comments to CMS regarding efforts to effectively manage chronic pain. Recognizing that limb loss is not uncommon and becoming less common every day, we know that no amputee should go through life alone on a quest to live well with limb loss. One of our priorities is to advocate with policymakers and stakeholders to ensure that the limb loss and limb difference community has a voice in important matters.
This community is uniquely impacted by chronic pain directly related to amputation or through secondary conditions that manifest due to living with limb loss. Pain management not only has a deleterious impact on physical health, but it is also inextricably intertwined with a person’s mental health. Properly addressing pain management is not only key for this nation’s physical health but also essential for its mental health.
The statistics related to misused prescription drugs are staggering. In 2019, it was estimated that 9.7 million Americans aged 12 or older abused prescription painkillers.[1] Mayo Clinic reports that mental health concerns and stressful circumstances are known risk factors for opioid misuse and addiction.[2]
The National Limb Loss Resource Center (NLLRC) supports programs and publications designed to help people return to an active lifestyle and function as productive members of society. In our publication Introduction to Managing Pain, we identified the following pain often experienced by those within the limb loss community. These include:
- Phantom limb sensation (PLS)
- Residual limb pain (RLP
- Phantom limb pain (PLP)
Since PLP is a common phenomenon within the limb loss community, we also have published Managing Phantom Pain to assist members in enduring the painful sensations. Treatment of PLP may involve prescription opioids to combat the effects. However, there are alternative treatments for PLP.
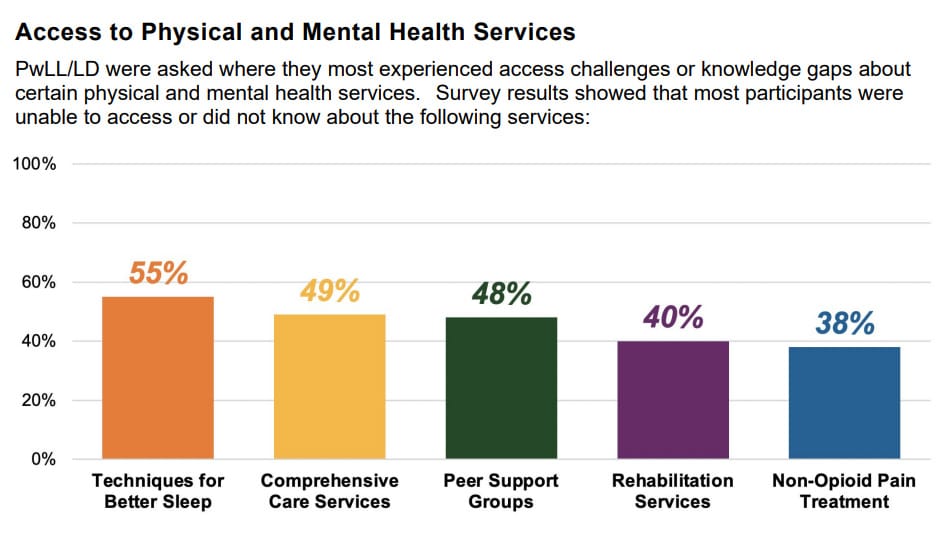
In April 2022, the Amputee Coalition released the results of the largest survey ever conducted for people with limb loss and limb difference. The survey consisting of over 1,700 participants identified the need for pain management as a key priority. Moreover, they recognized the relationship between physical and mental health, and the need to find age-appropriate solutions in the way healthcare is delivered. The survey also found that respondents of color more often reported access challenges to receiving comprehensive care, rehabilitation services, non-opioid pain treatment, and mental health services.
The Amputee Coalition truly applauds the efforts that CMS is making to properly address the way opioid prescriptions are administered. We fully recognize that the elimination of prescribed opioids is not a reasonable solution to pain management, however, we recognize that the administration of this treatment must be closely monitored to mitigate the risk of addiction. Due to the unique relationship the limb loss and limb difference community has to living with pain, we want to ensure we contribute to this conversation.
To learn more about the Amputee Coalition’s advocacy efforts, visit https://www.amputee-coalition.org/advocacy.
[1] Opioids in Medicare Part D: Concerns about Extreme Use and Questionable Prescribing (OEl-02-17-00250; 07/17) (hhs.gov)
[2] How opioid addiction occurs – Mayo Clinic

